Base technologies
Analyzing Urban Structures
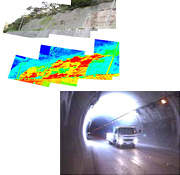
Inspecting and Diagnosing Structures
Japan’s stock of social capital reached nearly 800 trillion yen at the end of the 20th century. However, there are concerns about a shortage of social capital sources, including new investments, due to the prolonged recession, reductions in the number of children per family, and the aging and shrinking of the population.
Because of this situation, Japanese society will be shifting from an era of building to an era of maintaining/managing and renewal. Kokusai Kogyo is developing and providing new technologies for diagnosing/inspecting structures that will provide support for an era of maintenance/management. Based on information backed by highly reliable diagnostic/inspection technologies, we suggest appropriate repair/reinforcement measures and develop rational plans and designs intended to reduce lifecycle cost and ensure safety.
- Leveraging the expertise in spatial information/digital image processing that we have accumulated as a major aerial survey service provider, we are developing new inspection/diagnostic technologies.
- For inspecting structures, we are providing a sprayed-on slope face and bridge inspection system that uses thermal infrared video imaging, and a tunnel inspection technology that uses high-definition imaging. Because these systems are able not only to perform quantitative diagnosis and evaluation, but also to manage the inspection data as digital information, they can track changes that occur over time and provide the base data for subsequent inspections. A viewer function is also provided to allow the user to quickly search and display inspection results.
- We can inspect bridges in sync with the creation/updating of road registers by local municipalities, collect the base data that can be used for creating plans for repairing or extending the life of structures (bridges), and help them update their road management system databases.
- By introducing the latest repair/reinforcement technologies, we create optimum plans/designs in terms of both cost and benefit.
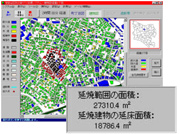
Fire Spread Simulation
"Fire spread simulation systems" are used in firefighting activities in order to rapidly predict fire spreading conditions based on actual weather conditions in order to assess what fire-fighting capabilities must be brought to bear, accurate team placement, and appropriate direction and management structures, in order to minimize the damages caused by multiple fires due to earthquakes, and in order to safely evacuate residents.
In order to take a safe town design approach which can be expected to prevent or delay the spread of fire, maintenance work must be facilitated in areas, especially densely populated urban areas, through the removal of burnable materials from along streets, securing open spaces, and the like. In order to increase disaster prevention awareness among residents, and promote resident-led development, "fire spread simulation systems" can also be used to provide scientific, objective information.
- The spread of fire from building to building is calculated based on past building fire and regional fire examples.
- Weather conditions, such as wind direction and speed, and fire spread conditions, such as building collapse ratios, can be entered as appropriate.
- Fire spread barrier lines, such as for wide roads, rivers, and the like, can be set as desired.
- Databases can be created in advance containing the structures and height of buildings owned by related organizations, information concerning factors that contribute to the spread of fire (hazardous facilities, flammable gas facilities, etc.), building spacing information obtainable from maps, and fire spread patterns for building types, making it possible to perform calculations in an extremely short period of time.
Evacuation Simulation
In most cases of evacuation due to increased volcanic activity or volcanic eruptions, cars are used. Volcanic areas are tourist destinations, so both the vehicles of residents and of visitors must be factored in when considering traffic volume. Traffic jams formed on national roads when Mt. Usu erupted in 2000. The problems which may affect evacuations must be assessed before the evacuations are needed, and valid evacuation directions, etc. considered.
Kokusai Kogyo performs "vehicle evacuation forecast simulations," providing base data for the establishment of volcanic eruption and other evacuation systems and plans.
- Vehicle evacuation forecast simulations which take into account volcano characteristics and volcanic eruption scenarios can be performed.
- Problem areas (bottlenecks) affecting evacuations in times of volcanic eruption and the like can be determined.
- Required evacuation times for individual evacuation directions can be calculated.
- Base data for the establishment of volcanic eruption and other disaster evacuation systems and plans can be acquired.